Let’s create a simple website scraper that download the content of a web page and extract the content of the page. For this example, we will use the New York Times website as the source of the content. The scraper will extract the top 10 news headlines on the page and display them on the web page. The scraping is done using the Puppeteer headless browser and web application is deployed on Firebase functions.
1. Initialize a Firebase Function
Assuming that you have already created a Firebase project, you can initialize the Firebase functions in a local environment by running the following command:
mkdir scraper
cd scraper
npx firebase init functions
cd functions
npm install puppeteerFollow through the prompts to initialize the project. We are also installing the Puppeteer package from NPM to use the Puppeteer headless browser.
2. Create a Node.js Application
Create a new pptr.js file in the functions folder that will contain the application code for scraping the content of the page. The script will only download the HTML content of the page and block all images, stylesheets, videos and fonts to reduce the amount of time it takes to download the page.
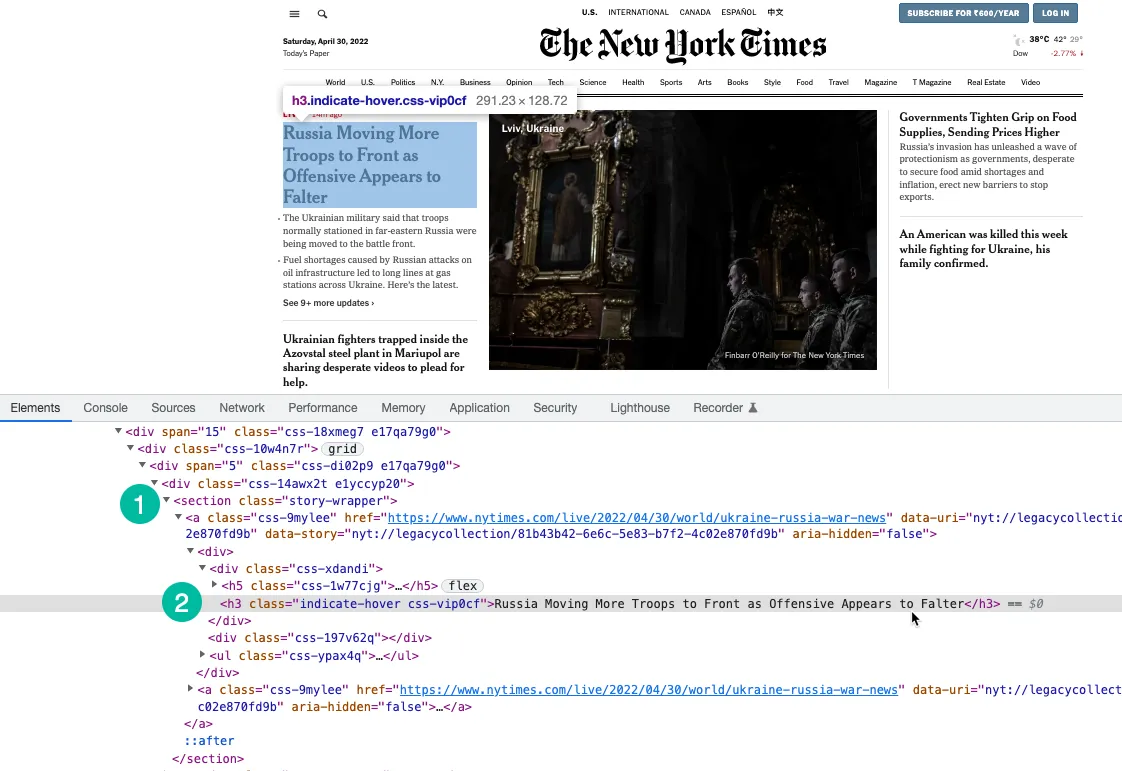
We are using XPath expression to select headlines on the page that are wrapped under the h3 tag. You may use Chrome Dev Tools to find the XPath of the headlines.
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
const scrapeWebsite = async () => {
let stories = [];
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
headless: true,
timeout: 20000,
ignoreHTTPSErrors: true,
slowMo: 0,
args: [
'--disable-gpu',
'--disable-dev-shm-usage',
'--disable-setuid-sandbox',
'--no-first-run',
'--no-sandbox',
'--no-zygote',
'--window-size=1280,720'
]
});
try {
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.setViewport({ width: 1280, height: 720 });
// Block images, videos, fonts from downloading
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
page.on('request', (interceptedRequest) => {
const blockResources = ['script', 'stylesheet', 'image', 'media', 'font'];
if (blockResources.includes(interceptedRequest.resourceType())) {
interceptedRequest.abort();
} else {
interceptedRequest.continue();
}
});
// Change the user agent of the scraper
await page.setUserAgent(
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4896.127 Safari/537.36'
);
await page.goto('https://www.nytimes.com/', {
waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded'
});
const storySelector = 'section.story-wrapper h3';
// Only get the top 10 headlines
stories = await page.$$eval(storySelector, (divs) =>
divs.slice(0, 10).map((div, index) => `${index + 1}. ${div.innerText}`)
);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
} finally {
if (browser) {
await browser.close();
}
}
return stories;
};
module.exports = scrapeWebsite;3. Write the Firebase Function
Inside the index.js file, import the scraper function and export it as a Firebase function. We are also writing a scheduled function that will run every day and will call the scraper function.
It is important to increase the function memory and time out limits as Chrome with Puppeteer is a heavy resource.
// index.js
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
const scrapeWebsite = require('./pptr');
exports.scrape = functions
.runWith({
timeoutSeconds: 120,
memory: '512MB' || '2GB'
})
.region('us-central1')
.https.onRequest(async (req, res) => {
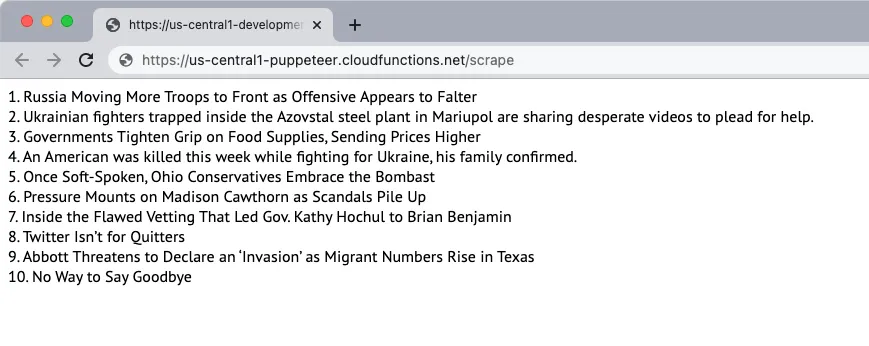
const stories = await scrapeWebsite();
res.type('html').send(stories.join('<br>'));
});
exports.scrapingSchedule = functions.pubsub
.schedule('09:00')
.timeZone('America/New_York')
.onRun(async (context) => {
const stories = await scrapeWebsite();
console.log('The NYT headlines are scraped every day at 9 AM EST', stories);
return null;
});4. Deploy the Function
If you wish to test the function locally, you may run the npm run serve command and navigate to the function endpoint on localhost. When you are ready to deploy the function to the cloud, the command is npm run deploy.
5. Test the Scheduled Function
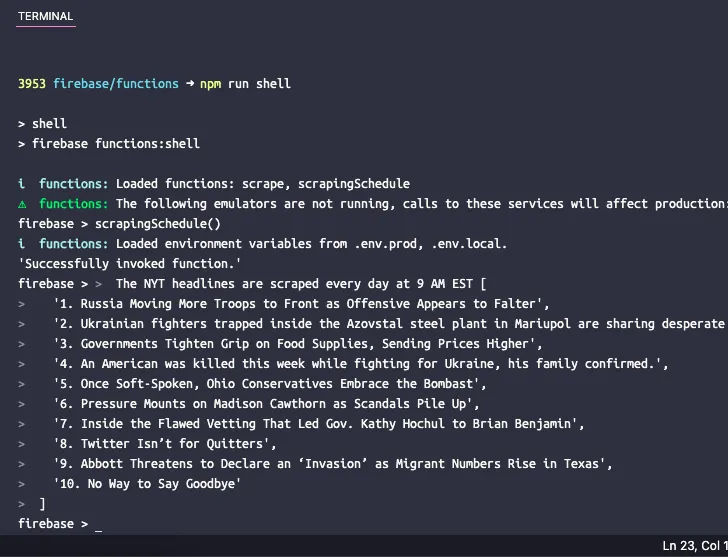
If you would like to test the scheduled function locally, you can run the command npm run shell to open an interactive shell for invoking functions manually with test data. Here type the function name scrapingSchedule() and hit enter to get the function output.