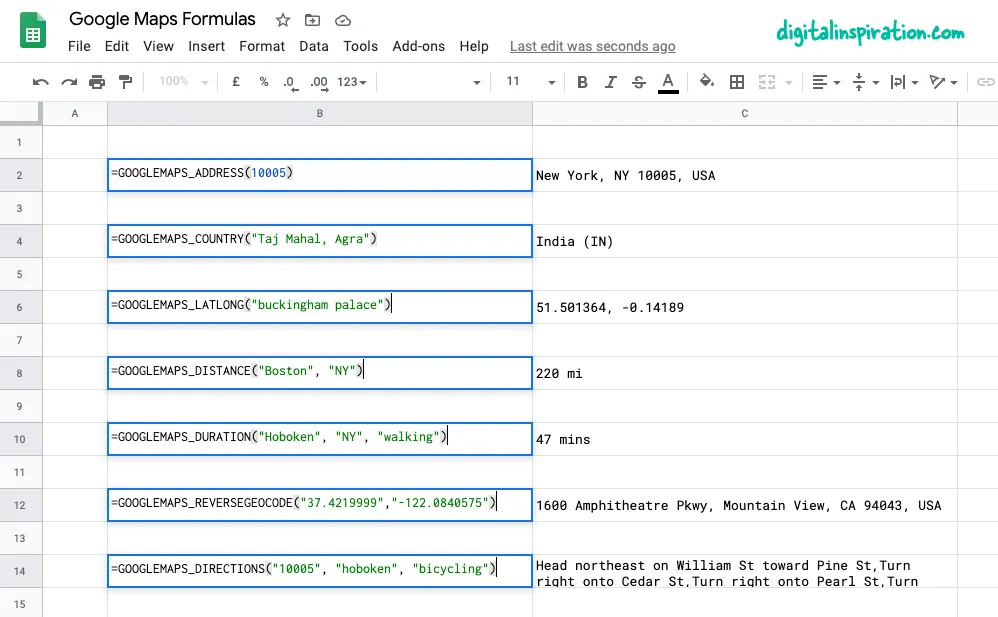
You can bring the power of Google Maps to your Google Sheets using simple formulas with no coding. You don’t need to sign-up for the Google Maps API and all results from Google Maps are cached in the sheet so you are unlikely to hit any quota limits.
To give you a quick example, if you have the starting address in column A and the destination address in column B, a formula like =GOOGLEMAPS_DISTANCE(A1, B1, "driving") will quickly calculate the distance between the two points.
Or modify the formula slightly =GOOGLEMAPS_TIME(A1, B1, "walking") to know how long it will take for a person to walk from one point to another.
If you would like to try the Google Maps formulas without getting into the technical details, just make a copy of this Google Sheet and you are all set.
Using Google Maps inside Google Sheets
This tutorial explains how you can easily write custom Google Maps functions inside Google Sheets that will help you:
- Calculate distances between two cities or any addresses.
- Calculate the travel time (walking, driving or biking) between two points.
- Get the latitude and longitude co-ordinates of any address on Google Maps.
- Use reverse geocoding to find the postal address from GPS co-ordinates.
- Print driving directions between any points on earth.
- Get the address from the zip code itself.
1. Calculate Distances in Google Sheets
Specify the origin, the destination, the travel mode (walking or driving) and the function will return the distance between the two points in miles.
=GOOGLEMAPS_DISTANCE("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
/**
* Calculate the distance between two
* locations on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_DISTANCE("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
*
* @param {String} origin The address of starting point
* @param {String} destination The address of destination
* @param {String} mode The mode of travel (driving, walking, bicycling or transit)
* @return {String} The distance in miles
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_DISTANCE = (origin, destination, mode) => {
const { routes: [data] = [] } = Maps.newDirectionFinder()
.setOrigin(origin)
.setDestination(destination)
.setMode(mode)
.getDirections();
if (!data) {
throw new Error('No route found!');
}
const { legs: [{ distance: { text: distance } } = {}] = [] } = data;
return distance;
};2. Reverse Geocoding in Google Sheets
Specify the latitude and longitude and get the full address of the point through reverse geocoding of coordinates.
=GOOGLEMAPS_DISTANCE("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
/**
* Use Reverse Geocoding to get the address of
* a point location (latitude, longitude) on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_REVERSEGEOCODE(latitude, longitude)
*
* @param {String} latitude The latitude to lookup.
* @param {String} longitude The longitude to lookup.
* @return {String} The postal address of the point.
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_REVERSEGEOCODE = (latitude, longitude) => {
const { results: [data = {}] = [] } = Maps.newGeocoder().reverseGeocode(latitude, longitude);
return data.formatted_address;
};3. Get the GPS coordinates of an address
Get the latitude and longitude of any address on Google Maps.
=GOOGLEMAPS_LATLONG("10 Hanover Square, NY")
/**
* Get the latitude and longitude of any
* address on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_LATLONG("10 Hanover Square, NY")
*
* @param {String} address The address to lookup.
* @return {String} The latitude and longitude of the address.
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_LATLONG = (address) => {
const { results: [data = null] = [] } = Maps.newGeocoder().geocode(address);
if (data === null) {
throw new Error('Address not found!');
}
const { geometry: { location: { lat, lng } } = {} } = data;
return `${lat}, ${lng}`;
};4. Print the driving directions between addresses
Specify the origin address, the destination address, the travel mode and the function will use the Google Maps API to print step-by-step driving directions.
=GOOGLEMAPS_DIRECTIONS("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
/**
* Find the driving direction between two
* locations on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_DIRECTIONS("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
*
* @param {String} origin The address of starting point
* @param {String} destination The address of destination
* @param {String} mode The mode of travel (driving, walking, bicycling or transit)
* @return {String} The driving direction
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_DIRECTIONS = (origin, destination, mode = 'driving') => {
const { routes = [] } = Maps.newDirectionFinder()
.setOrigin(origin)
.setDestination(destination)
.setMode(mode)
.getDirections();
if (!routes.length) {
throw new Error('No route found!');
}
return routes
.map(({ legs }) => {
return legs.map(({ steps }) => {
return steps.map((step) => {
return step.html_instructions.replace(/<[^>]+>/g, '');
});
});
})
.join(', ');
};5. Measure the trip time with Google Maps
Specify the origin address, the destination address, the travel mode and the function will measure your approximate trip time between the specified addresses, provided a route exists.
=GOOGLEMAPS_DURATION("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
/**
* Calculate the travel time between two locations
* on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_DURATION("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
*
* @param {String} origin The address of starting point
* @param {String} destination The address of destination
* @param {String} mode The mode of travel (driving, walking, bicycling or transit)
* @return {String} The time in minutes
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_DURATION = (origin, destination, mode = 'driving') => {
const { routes: [data] = [] } = Maps.newDirectionFinder()
.setOrigin(origin)
.setDestination(destination)
.setMode(mode)
.getDirections();
if (!data) {
throw new Error('No route found!');
}
const { legs: [{ duration: { text: time } } = {}] = [] } = data;
return time;
};
Tip: Improve Formula Performance by Caching
The Google Sheets functions internally use the Google Maps API to calculate routes, distances and travel time. Google offers a limited quota for Maps operations and if your sheet performs too many queries in a short duration, you are likely to see errors like ""Service invoked too many times for one day” or something similar.
To get around the quota issue, it is recommended that you use Apps Script’s built-in cache to store results and, if the results of a function already exist in the case, you’ll make one less request to Google Maps.
The Maps functions inside this Google Sheet also use caching and here’s how you can implement it.
// The cache key for "New York" and "new york " should be same
const md5 = (key = '') => {
const code = key.toLowerCase().replace(/\s/g, '');
return Utilities.computeDigest(Utilities.DigestAlgorithm.MD5, key)
.map((char) => (char + 256).toString(16).slice(-2))
.join('');
};
const getCache = (key) => {
return CacheService.getDocumentCache().get(md5(key));
};
// Store the results for 6 hours
const setCache = (key, value) => {
const expirationInSeconds = 6 * 60 * 60;
CacheService.getDocumentCache().put(md5(key), value, expirationInSeconds);
};
/**
* Calculate the travel time between two locations
* on Google Maps.
*
* =GOOGLEMAPS_DURATION("NY 10005", "Hoboken NJ", "walking")
*
* @param {String} origin The address of starting point
* @param {String} destination The address of destination
* @param {String} mode The mode of travel (driving, walking, bicycling or transit)
* @return {String} The time in minutes
* @customFunction
*/
const GOOGLEMAPS_DURATION = (origin, destination, mode = 'driving') => {
const key = ['duration', origin, destination, mode].join(',');
// Is result in the internal cache?
const value = getCache(key);
// If yes, serve the cached result
if (value !== null) return value;
const { routes: [data] = [] } = Maps.newDirectionFinder()
.setOrigin(origin)
.setDestination(destination)
.setMode(mode)
.getDirections();
if (!data) {
throw new Error('No route found!');
}
const { legs: [{ duration: { text: time } } = {}] = [] } = data;
// Store the result in internal cache for future
setCache(key, time);
return time;
};

